

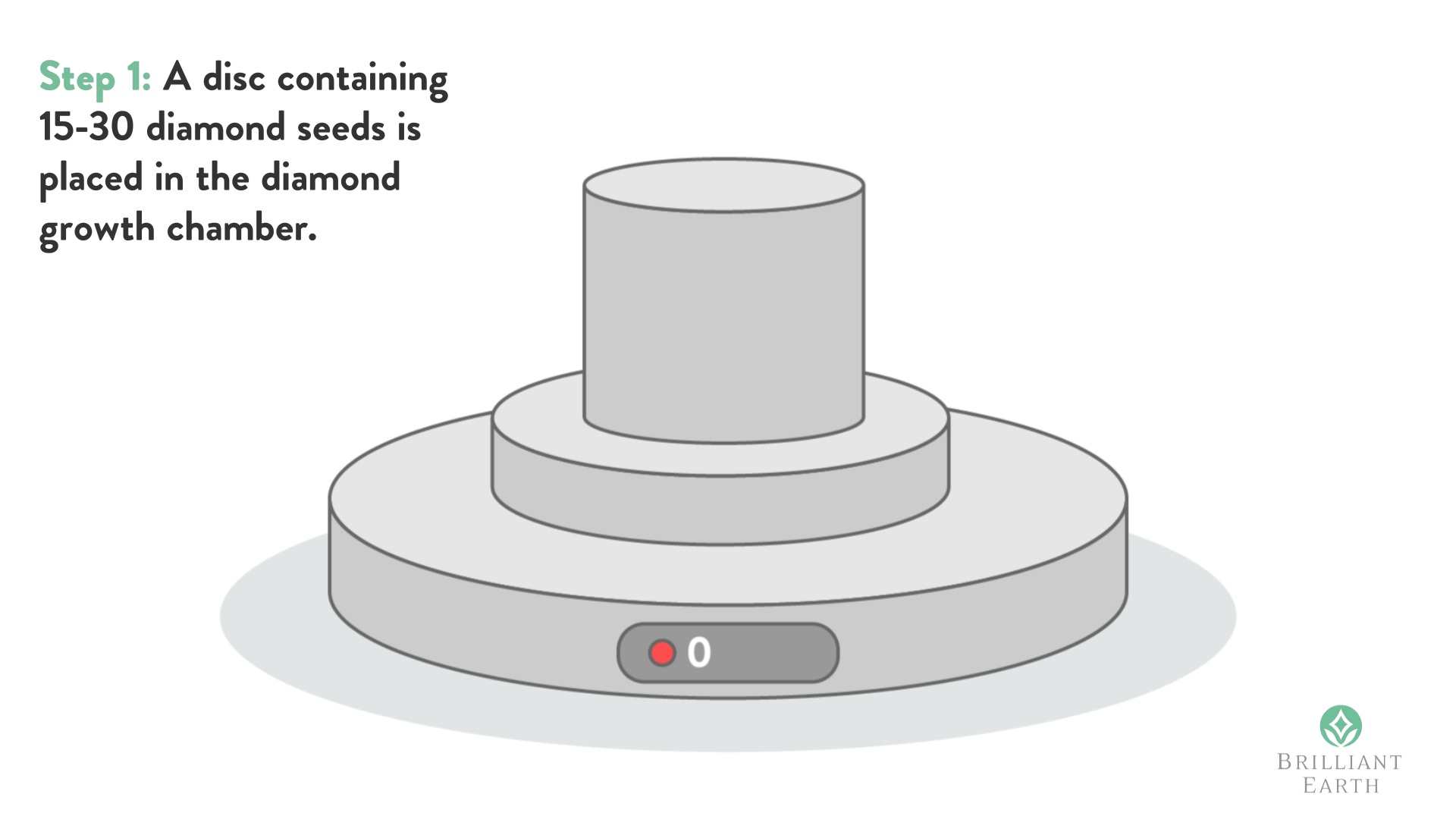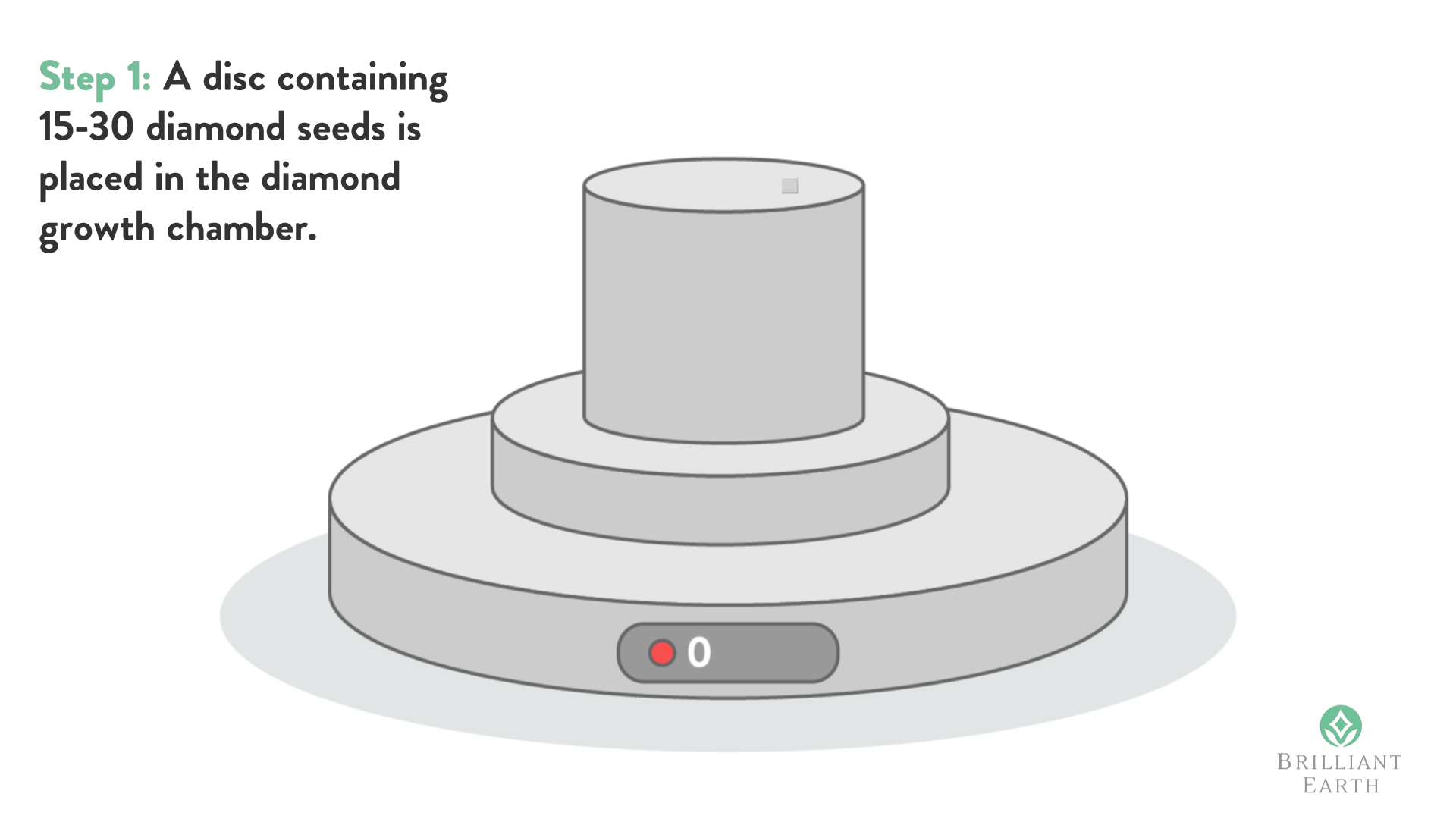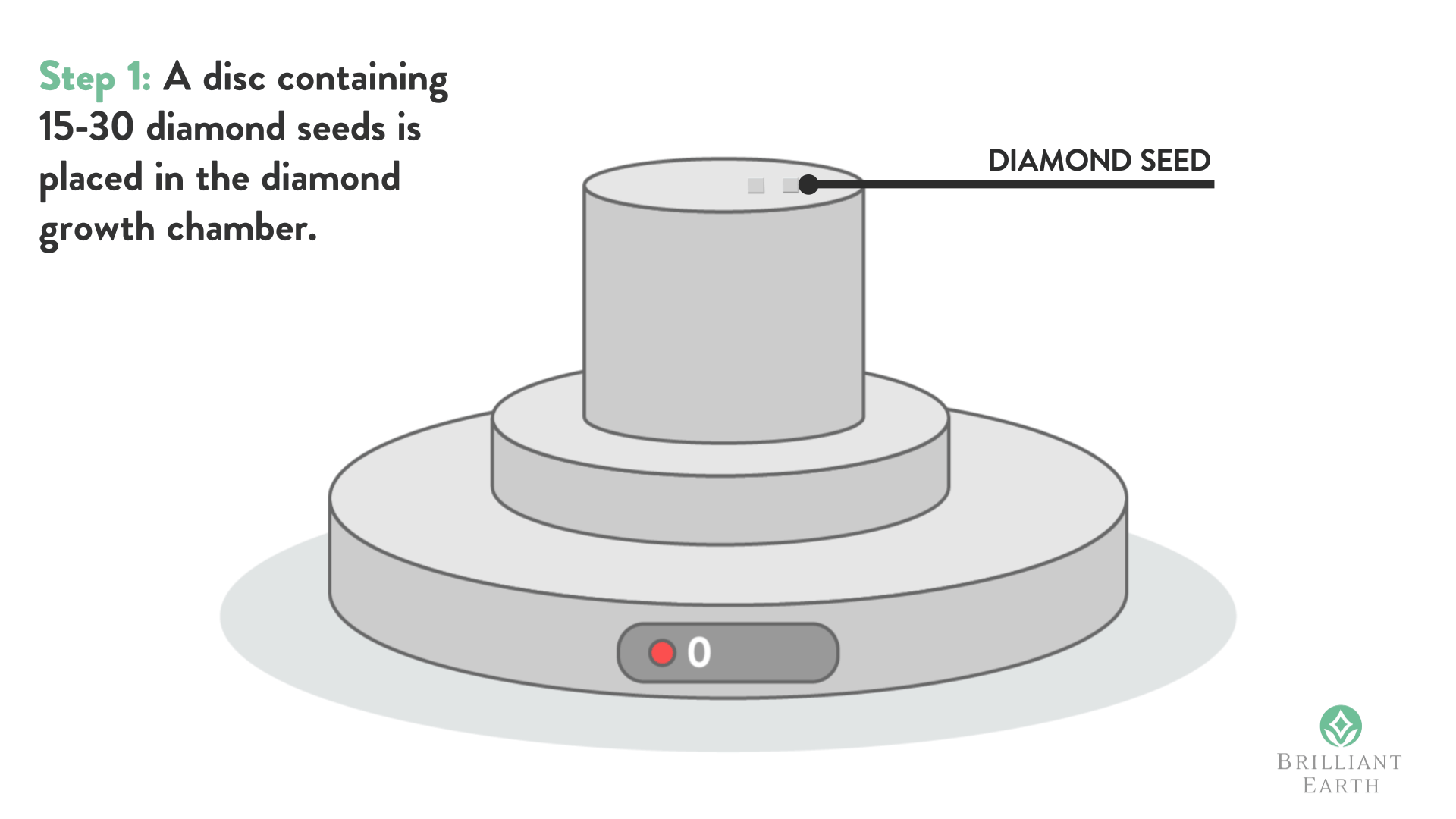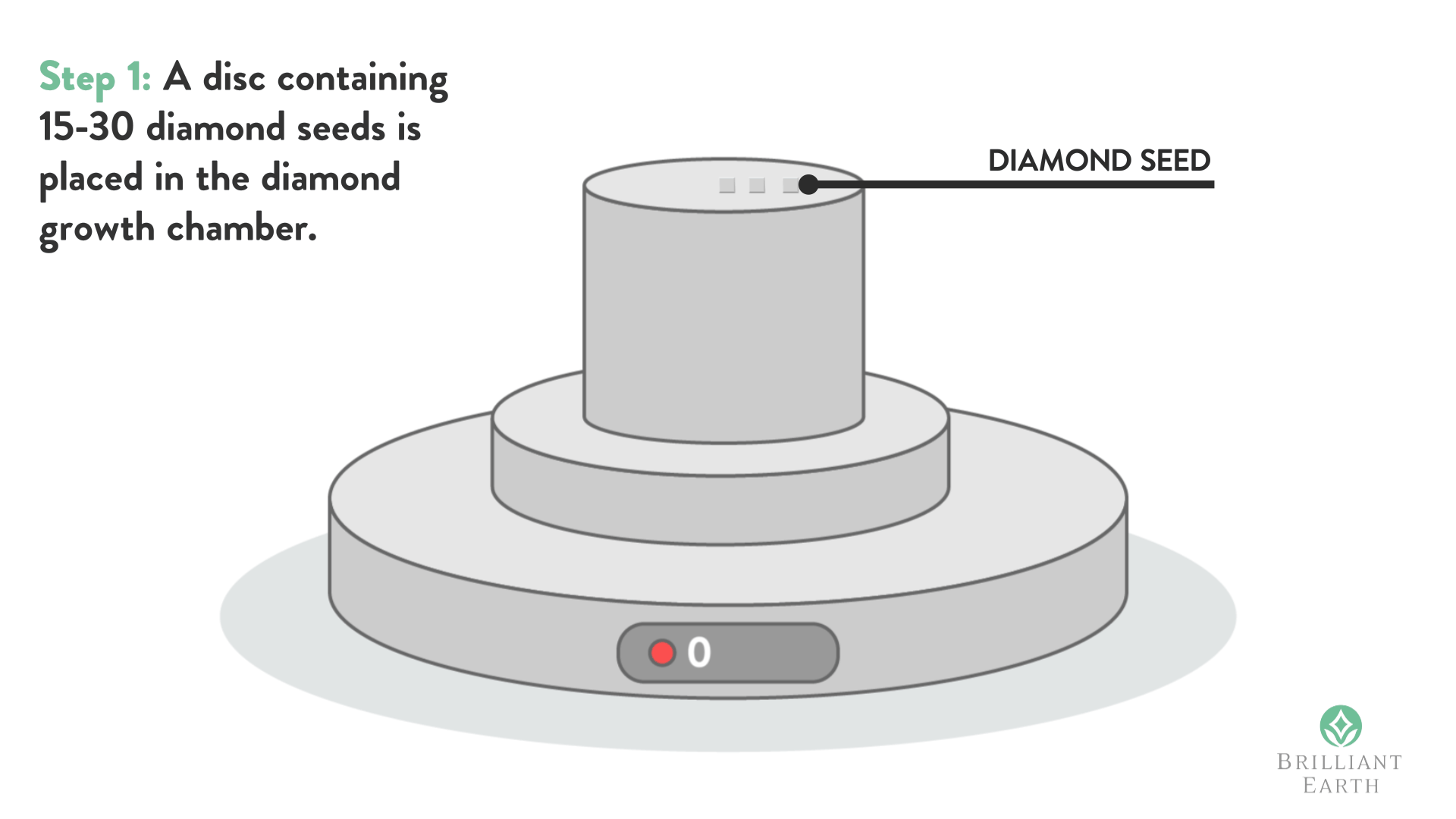
Diamond seed is when you take a very small part of the diamond (Usually with the best strongest property growing pattern) to grow synthetic diamonds in the labs. As you may be aware Synthetic diamonds came long back, so they have been taking “Diamond Seeds” from the actual diamonds since a very long time back.
The characteristics of diamond synthesis by microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition (CVD) under pressures greater than atmospheric pressure were investigated. The deposits on Si substrates were identified by scanning electron microscopy and Raman spectroscopy.
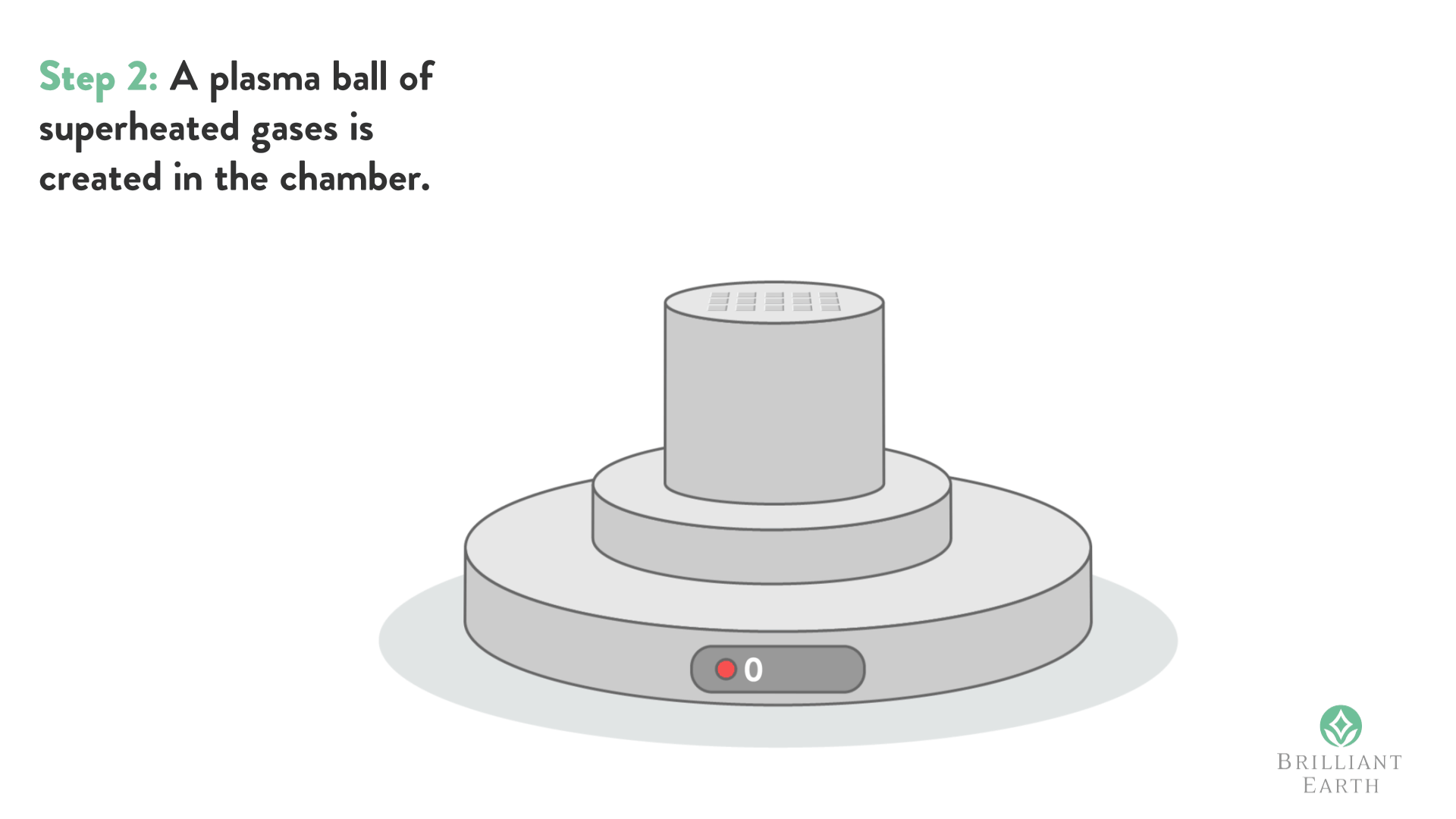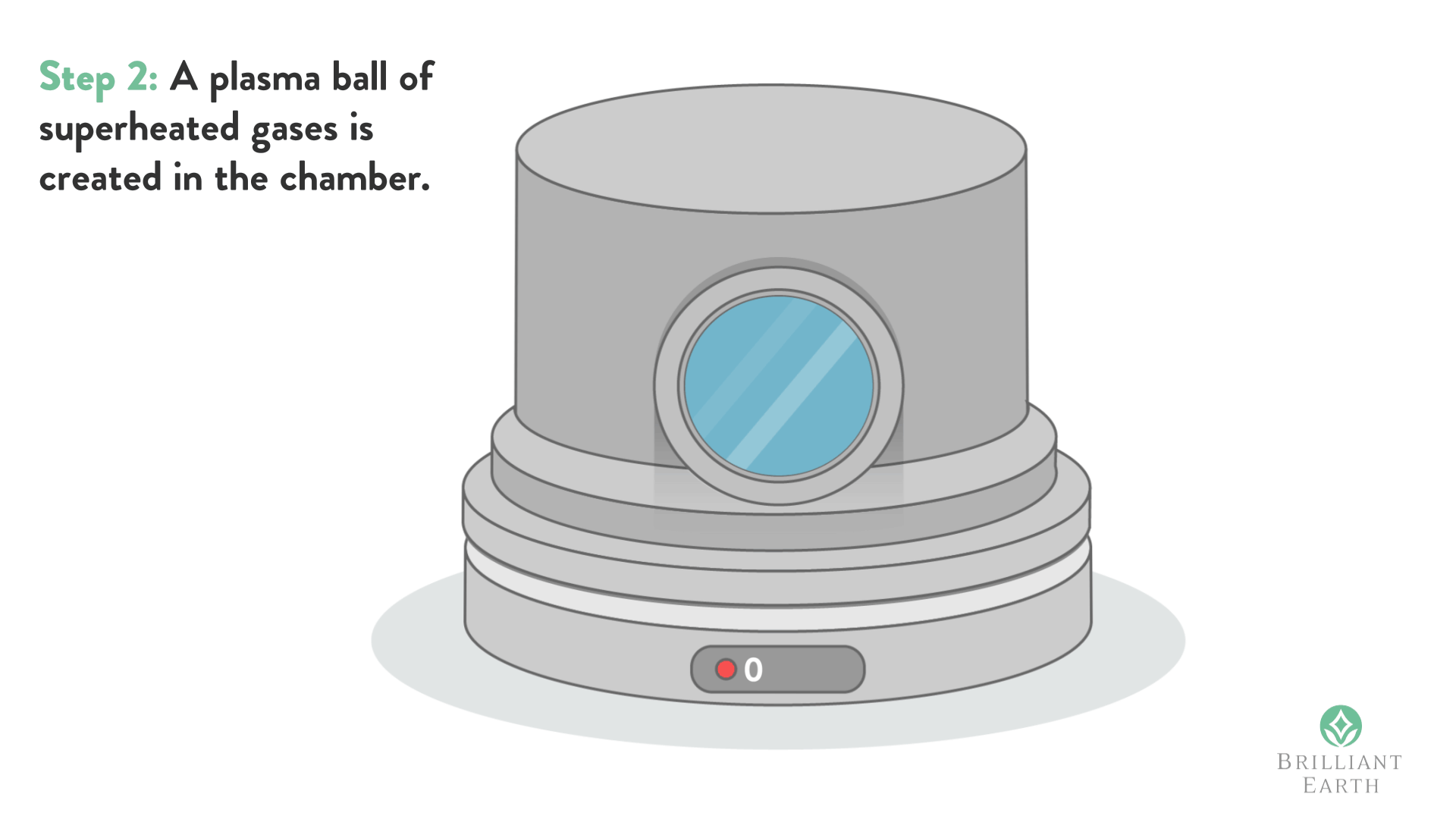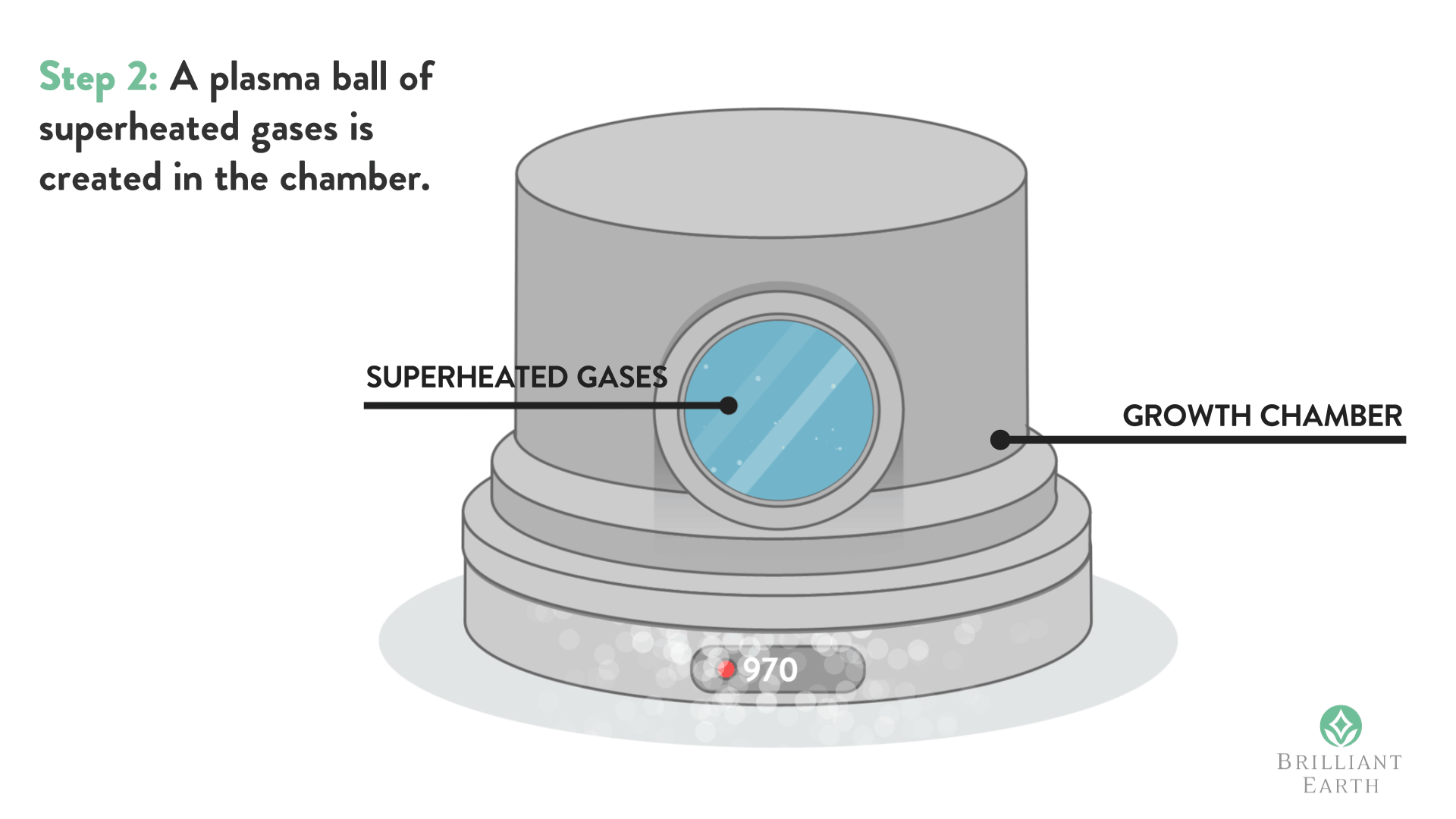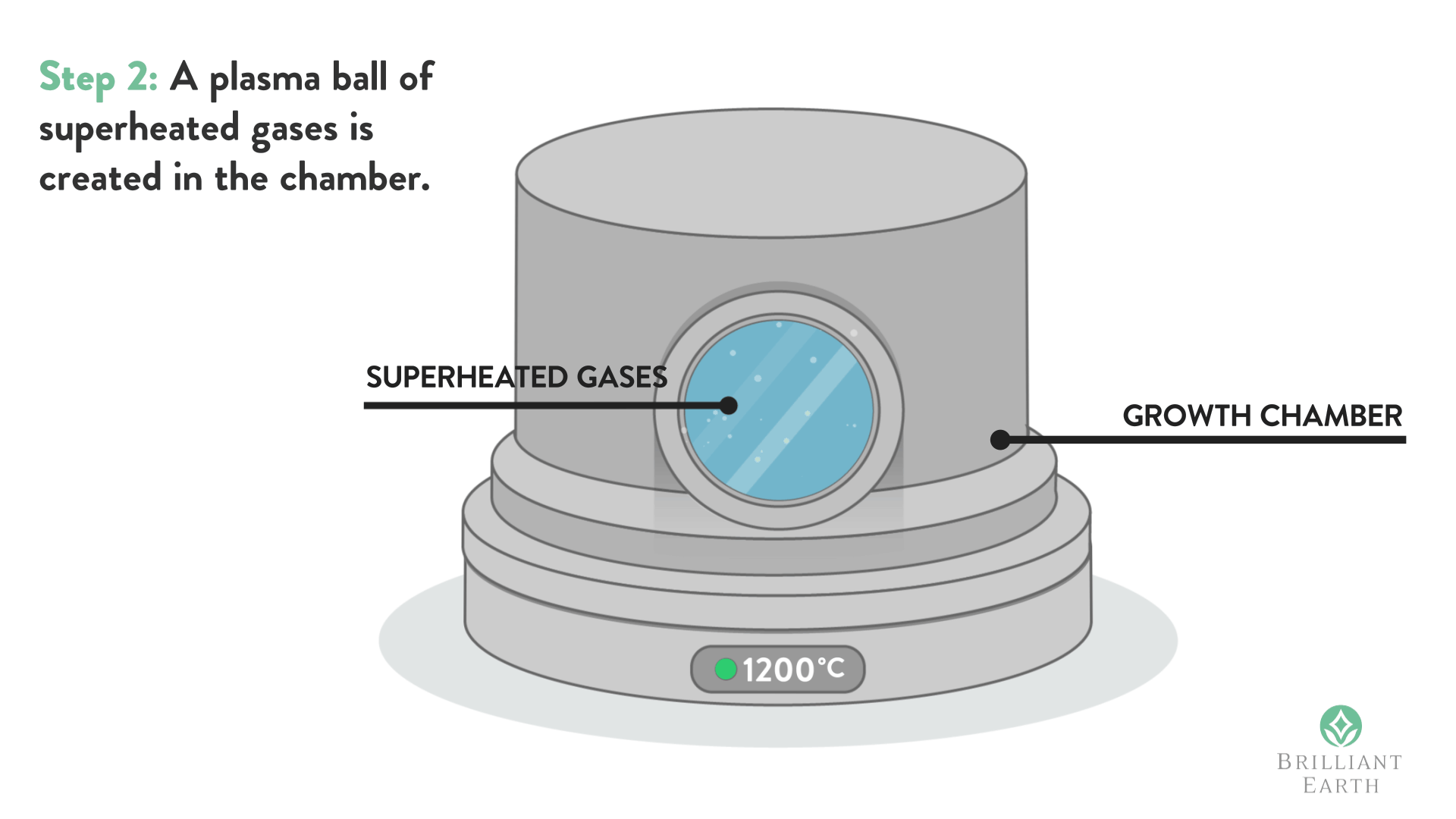
The process then provides the use of separate sealed vessels wherein the diamonds are respectively submerged in strong caustic and acid solvents, and heated to high temperature. with associated high vaporous pressures, for durations of possibly more than a day.
The hard amorphous hydrogenated carbon films (a-C:H) belong to the class of materials called diamond-like carbon (DLC). These materials are designated as DLC due to their superlative properties, similar to that of crystalline diamond, such as high hardness, low friction coefficient, high chemical and wear resistance, and high electrical resistivity.
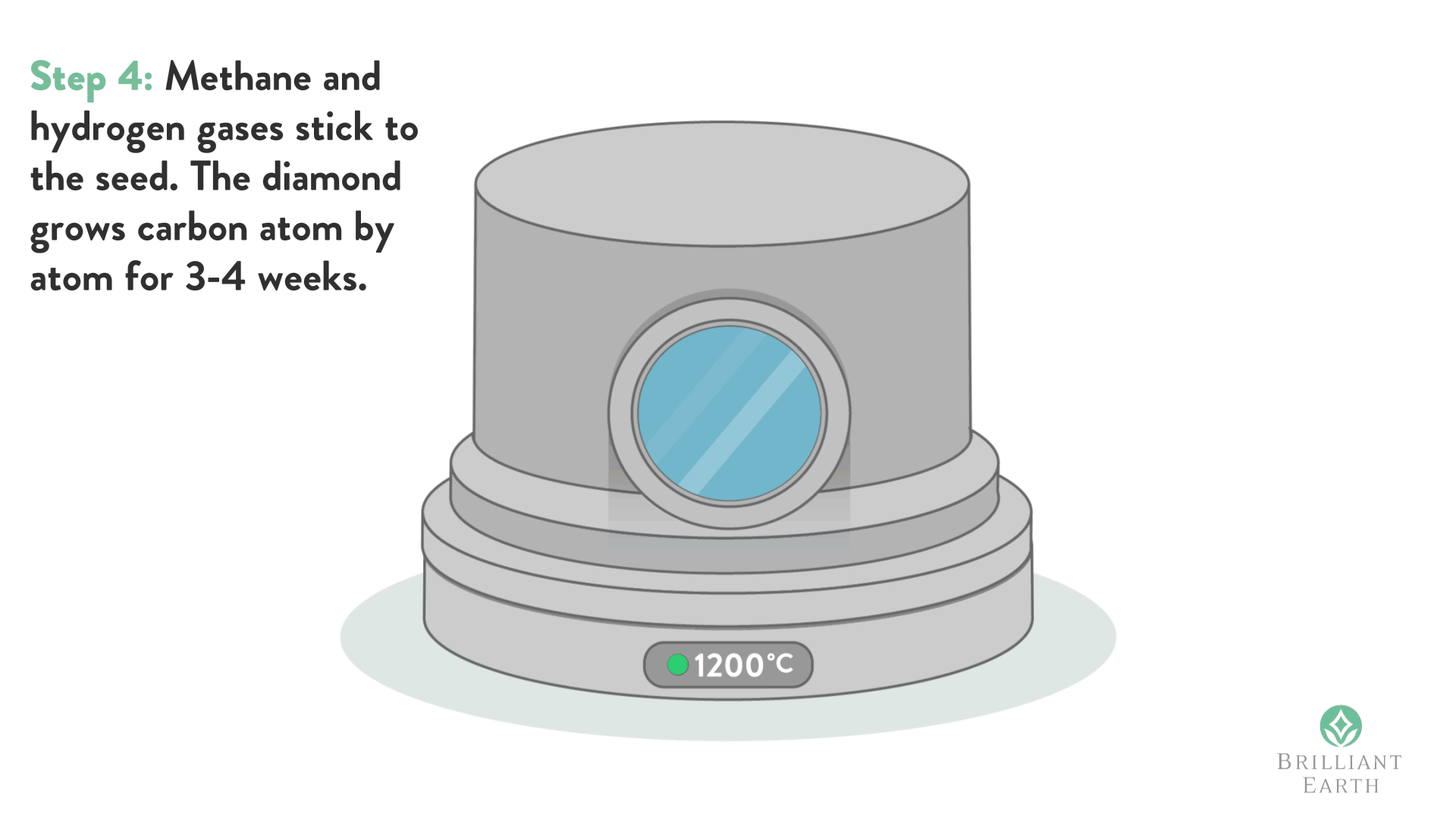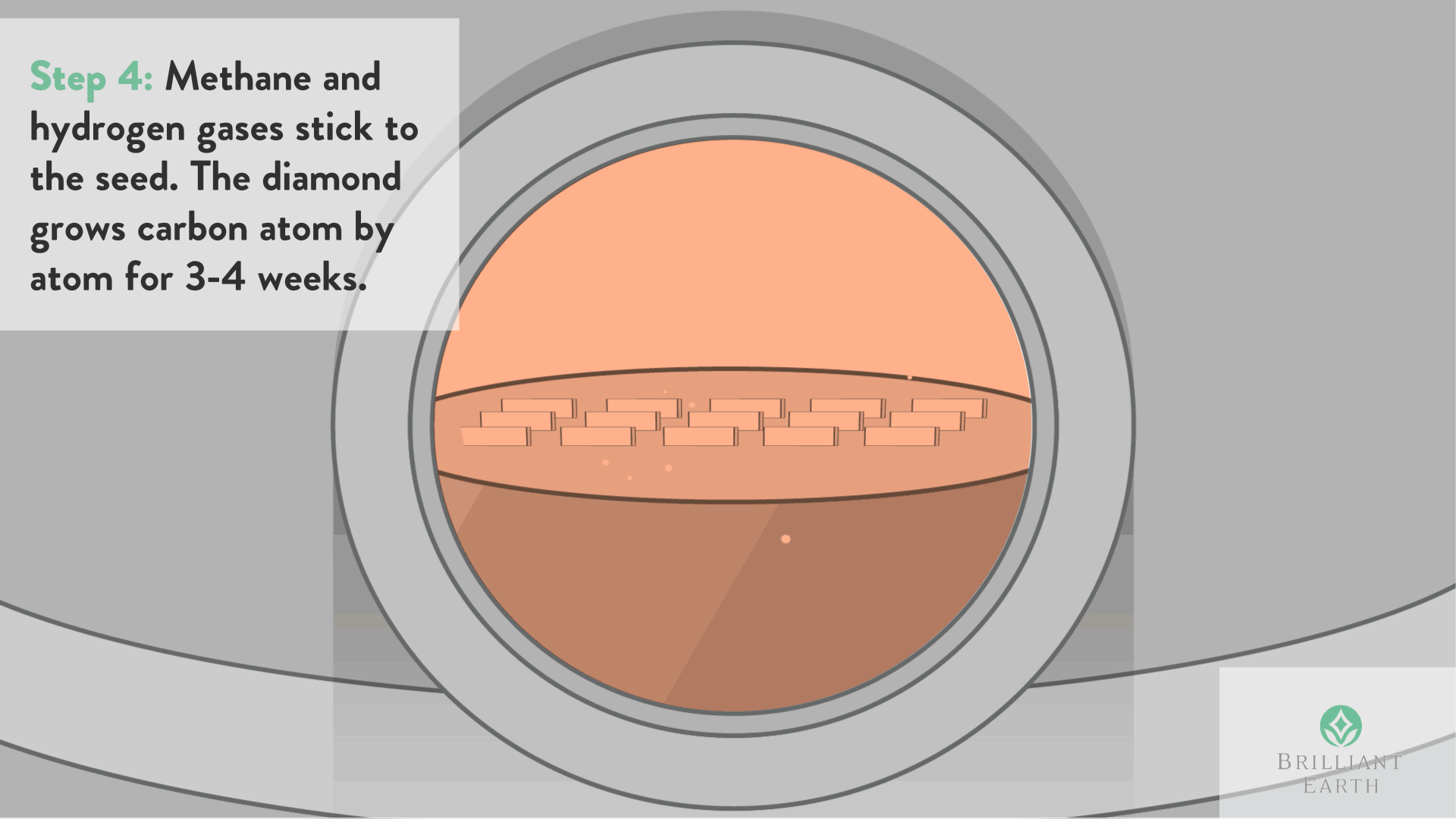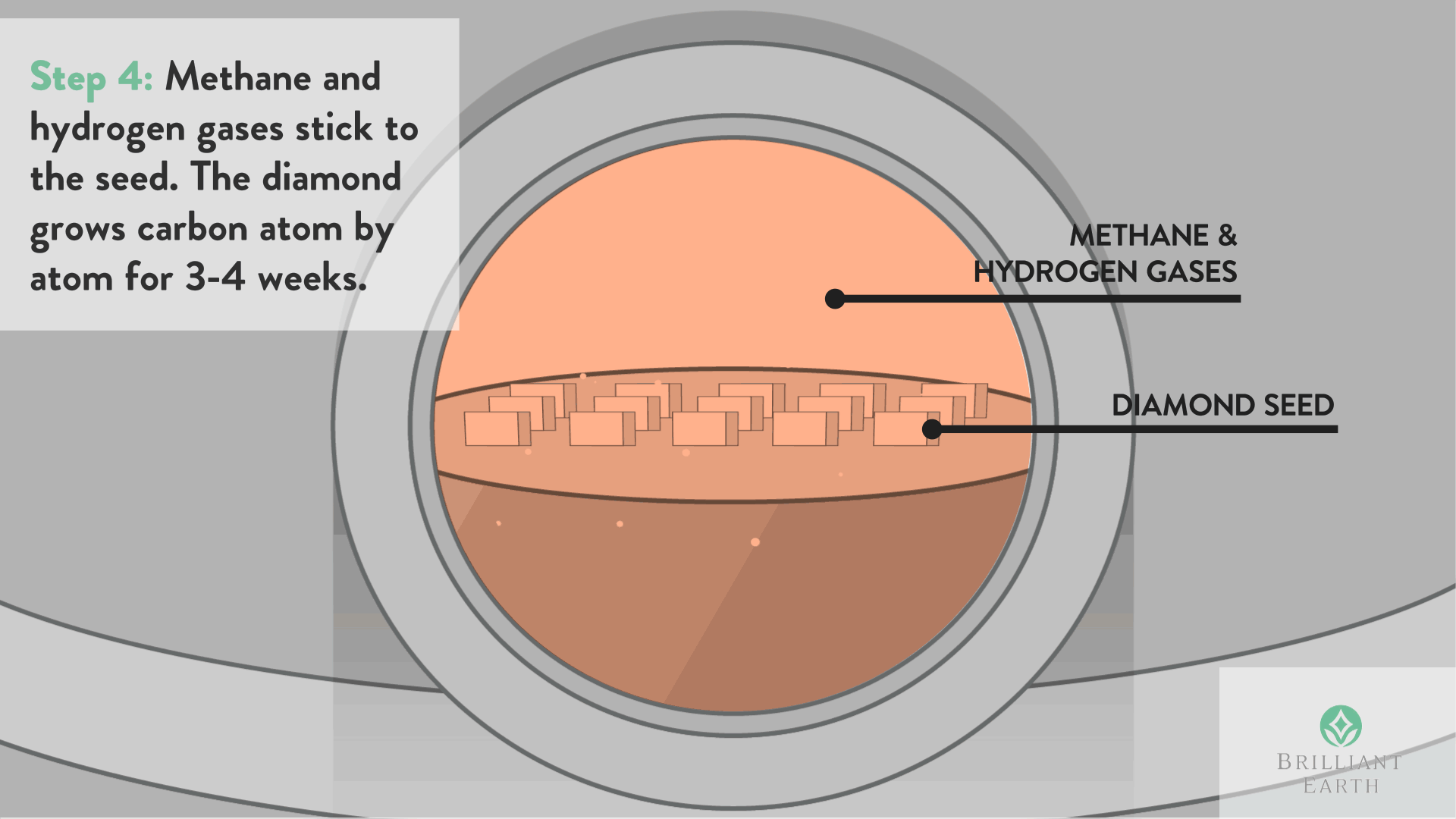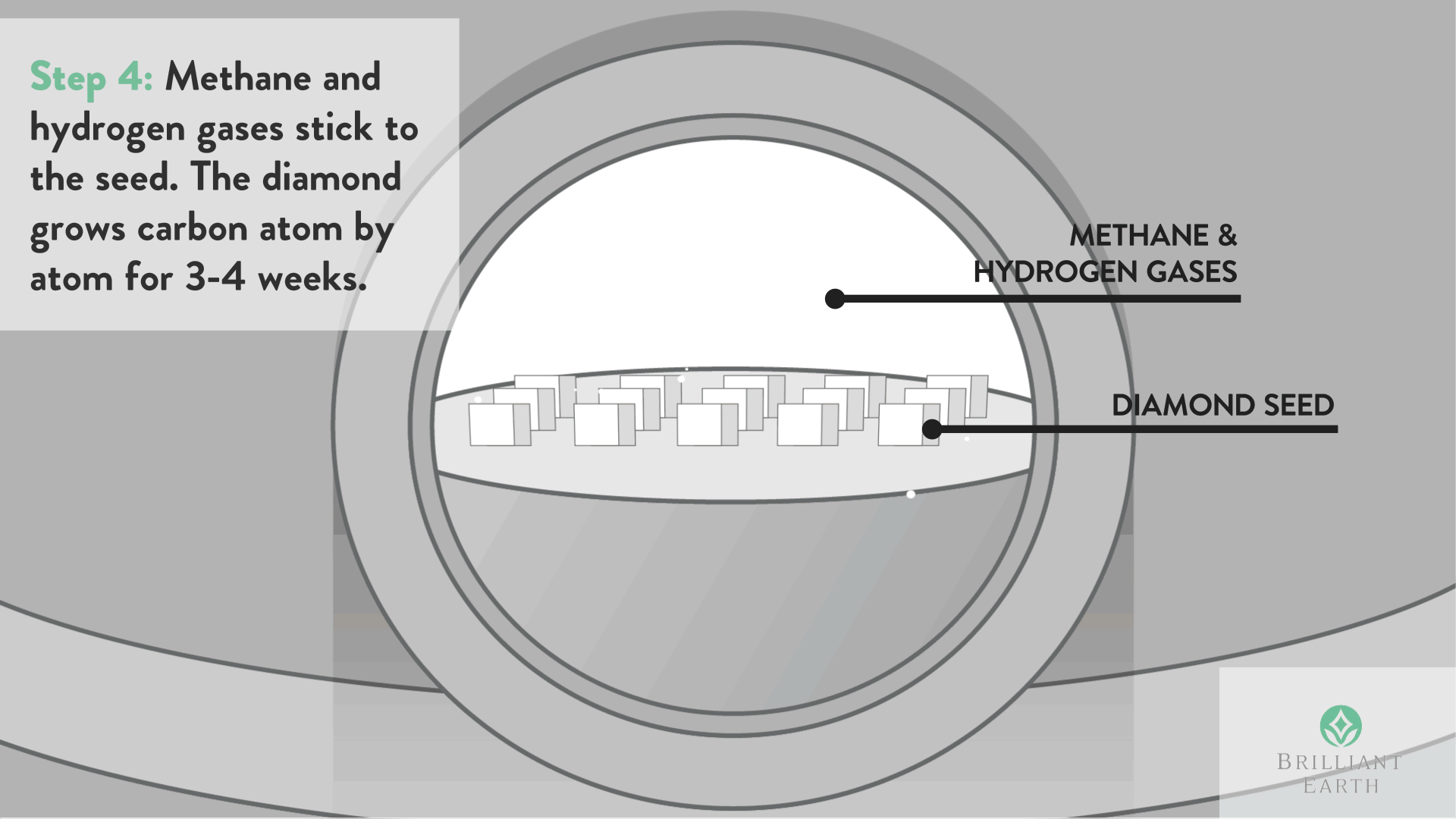

The method includes a step of heating the diamond-coated body at a predetermined temperature in a reactor at a predetermined reduced pressure, while introducing an oxygen gas into the reactor at a predetermined flow rate, for burning the diamond coating to thereby remove the diamond coating from the substrate.
The five basic steps to cutting a diamond are: sorting the rough, planning for manufacturing, cleaving or sawing the rough into a preliminary shape, shaping the girdle, and polishing the facets. Decisions at every step of the process affect the value of the final polished gem.
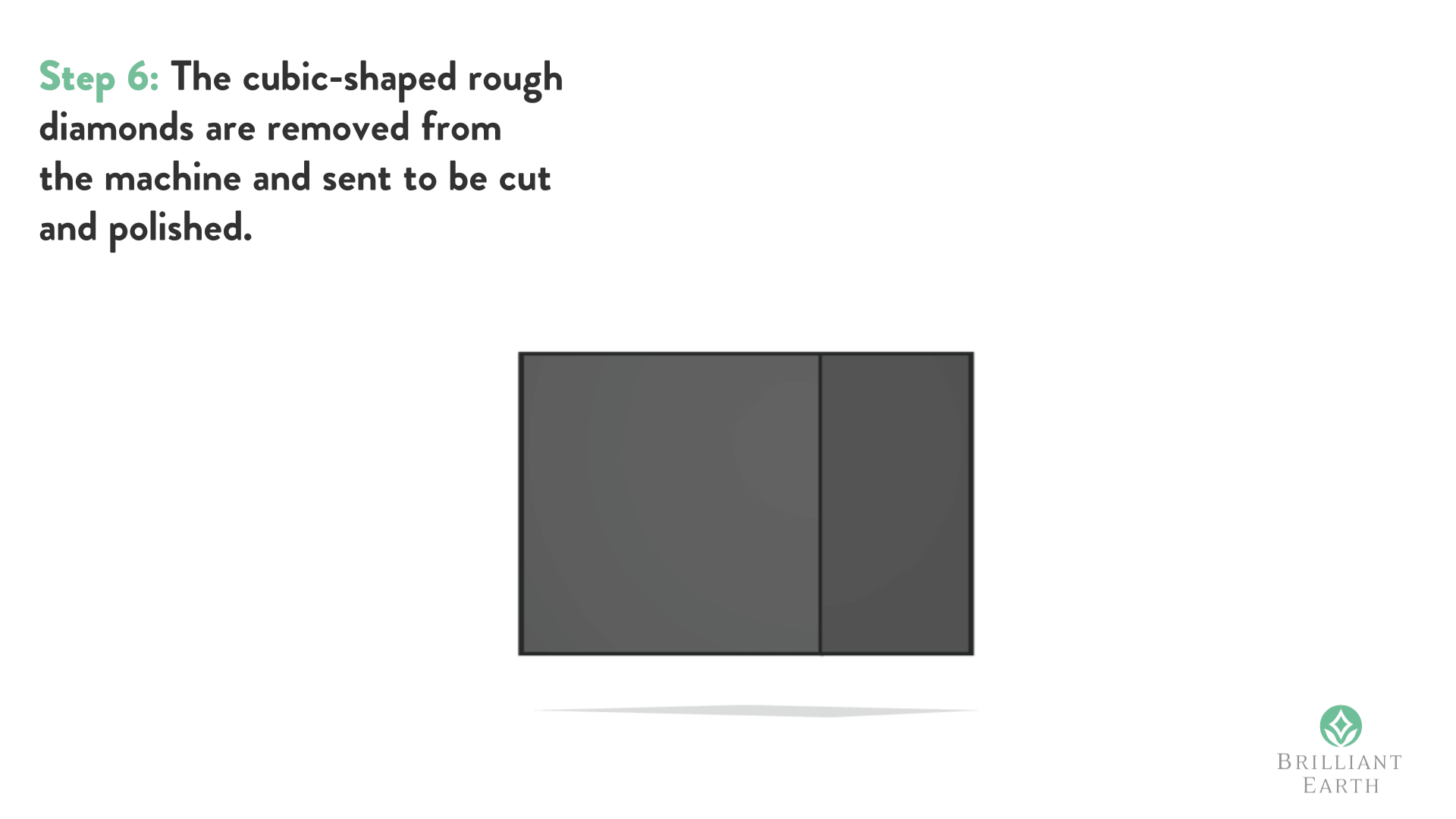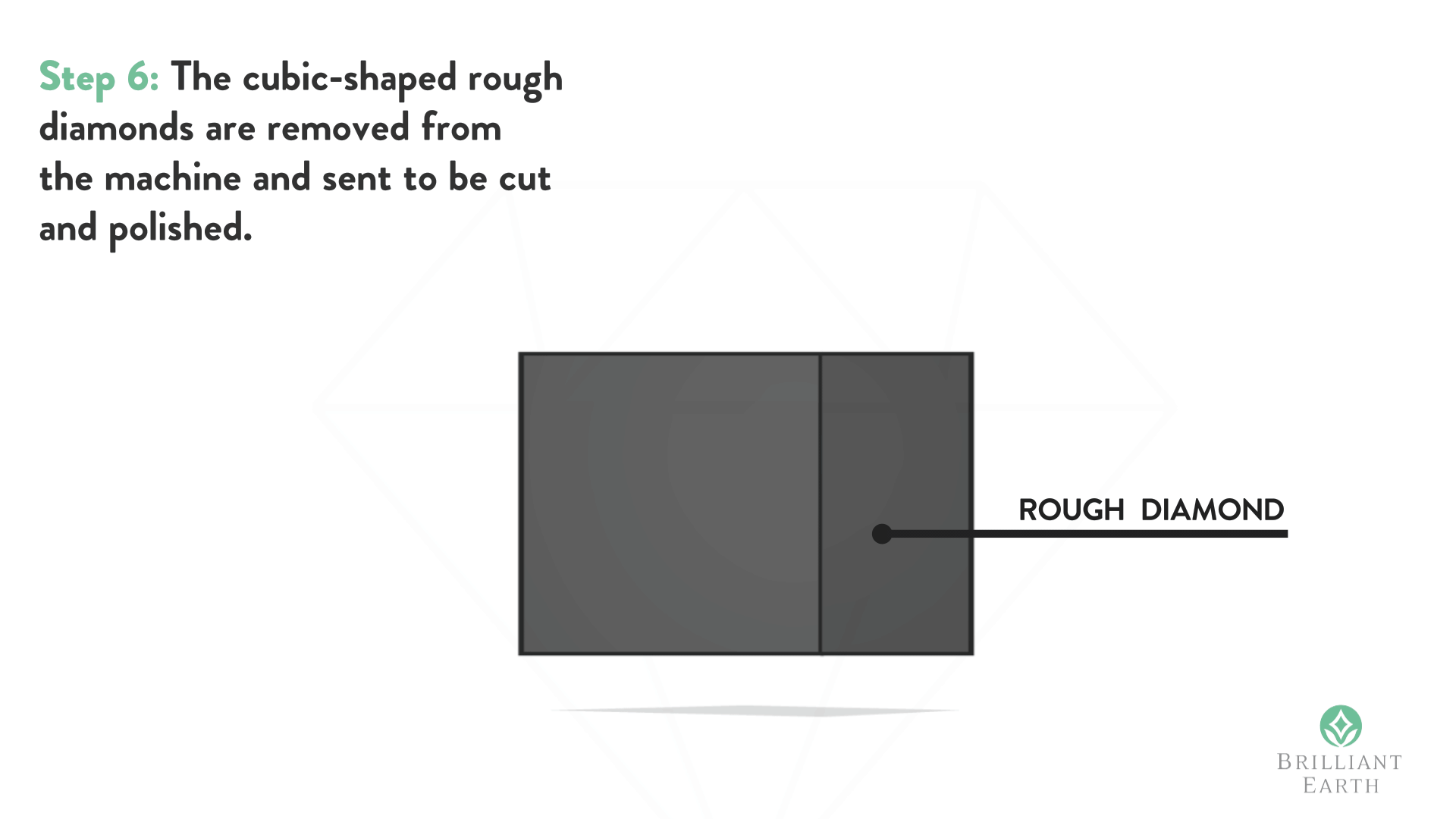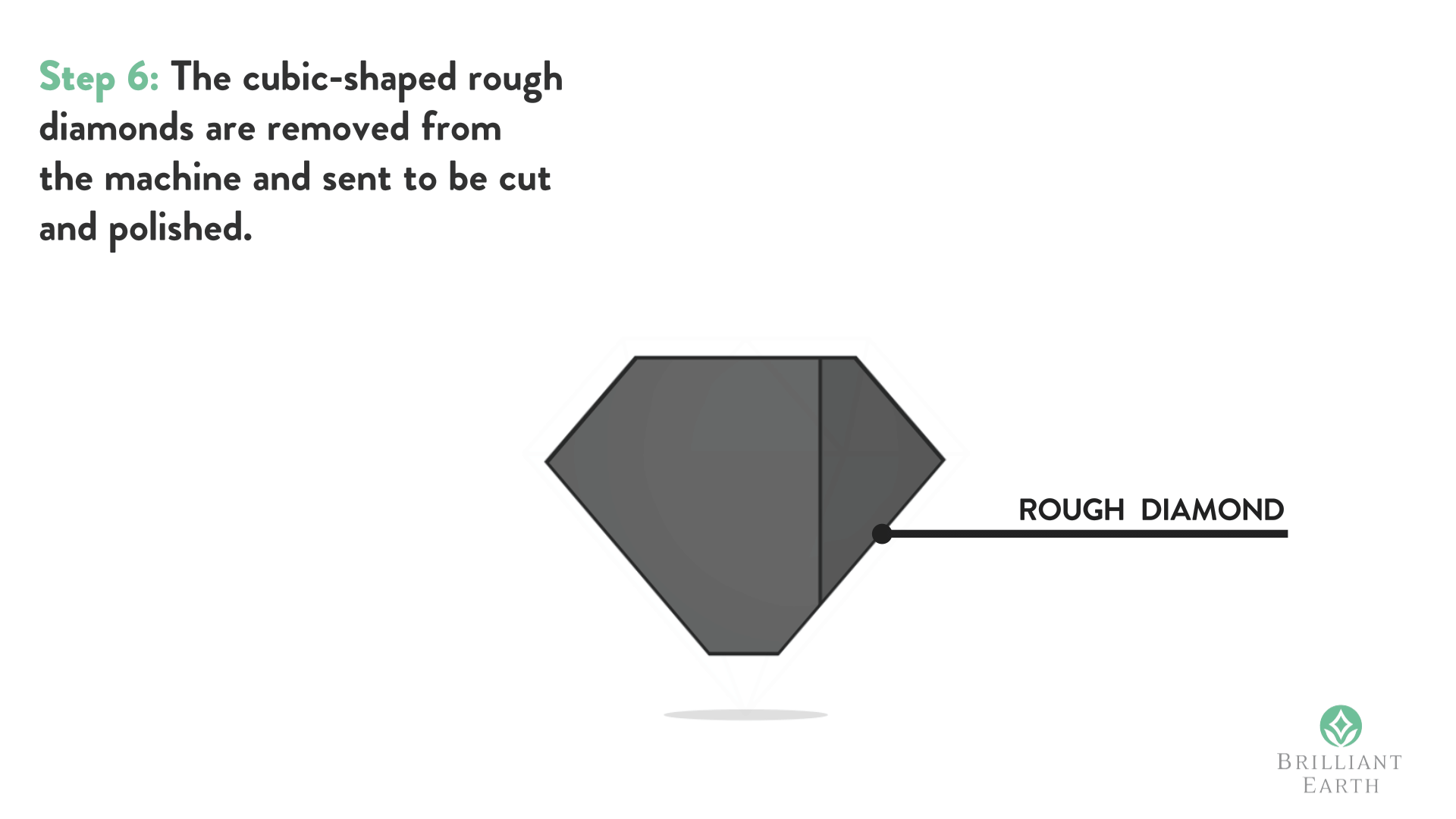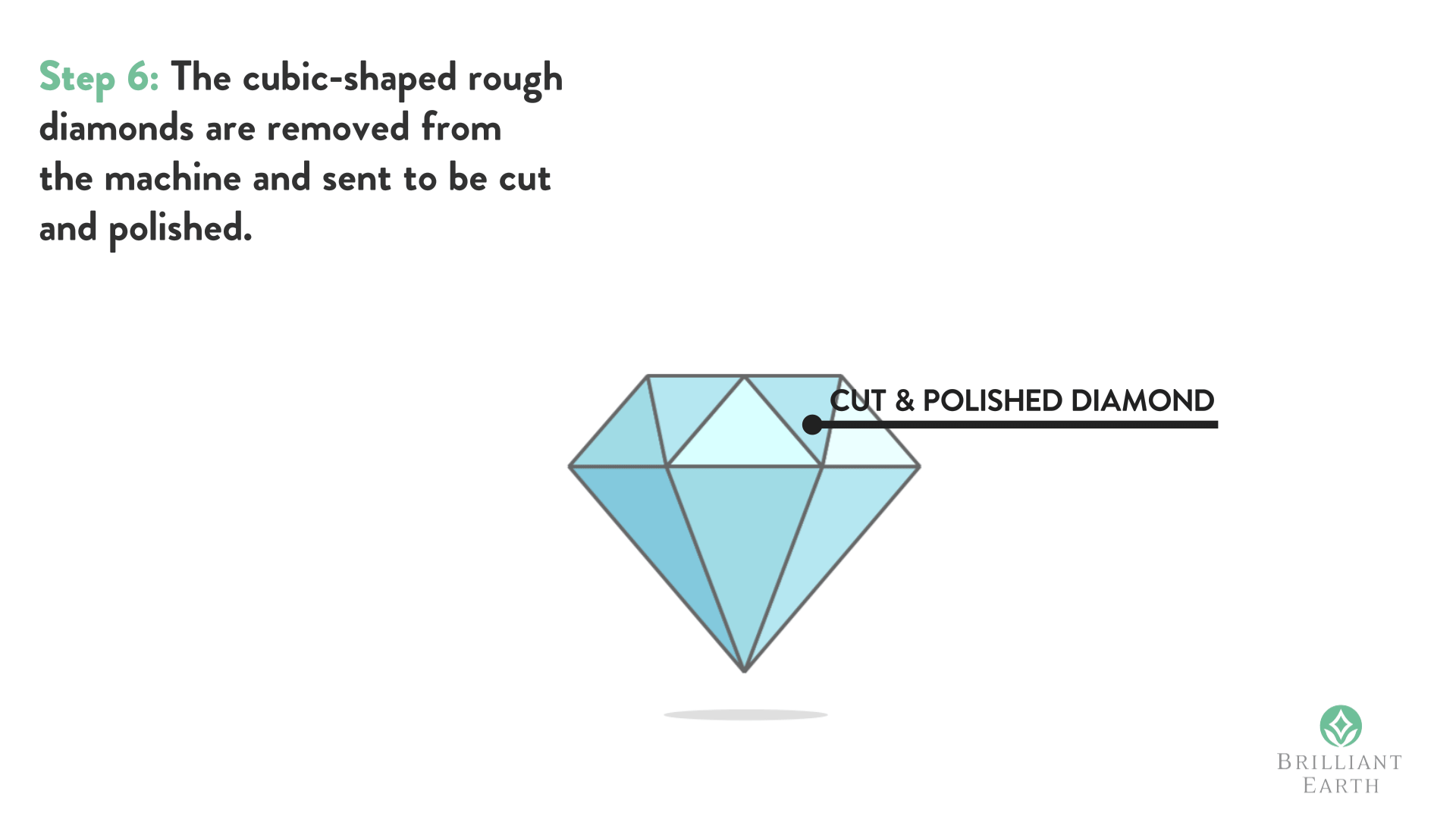
The only thing that makes a lab-grown diamond different from a natural diamond is its origin. A lab-grown diamond is “grown” inside a lab using cutting-edge technology that replicates the natural diamond growing process. The result is a man-made diamond that is chemically, physically, and optically the same as those grown beneath the Earth’s surface.
| Diamonds | Natural Diamond | Lab Grown Diamond |
|---|---|---|
Design |

|

|
Color |
F |
F |
Weight |
1.01 |
1.01 |
Clarity |
VS1 |
VS1 |
Price |
6000 $ (Very Expensive) |
1500 $ (Less Expensive) |
Buy Back Value |
4200 $ (1800 $ Loss) |
Can use free for lifetime no need resale |
The Above Table Clearly Shows That Mined Diamonds Are More Expensive than Lab-Grown Diamonds, and Mined Diamonds Do Not Get Much Buyback Value. Lab grown stones cost less than traditional mined diamonds because they require less mining, processing and cutting.